As we step into 2025, understanding the updated Income Tax Slab for 2025 becomes critical for taxpayers in India. In its pursuit of economic reforms and ease of compliance, the government has introduced changes to the tax structure. These changes simplify taxation while ensuring equitable contributions from all income groups. This article will delve into the new income tax slabs, their implications, and how they impact individuals and businesses.
What Are Income Tax Slabs?
India follows a progressive taxation system, where individuals are taxed based on their annual income. The income tax slabs determine the percentage of tax you need to pay based on your income bracket. This structure ensures that taxpayers with higher incomes contribute more to the government’s revenue.
Taxpayers can choose between:
- Old Tax Regime – Offers tax exemptions and deductions.
- New Tax Regime – Provides lower tax rates but eliminates most exemptions and deductions.
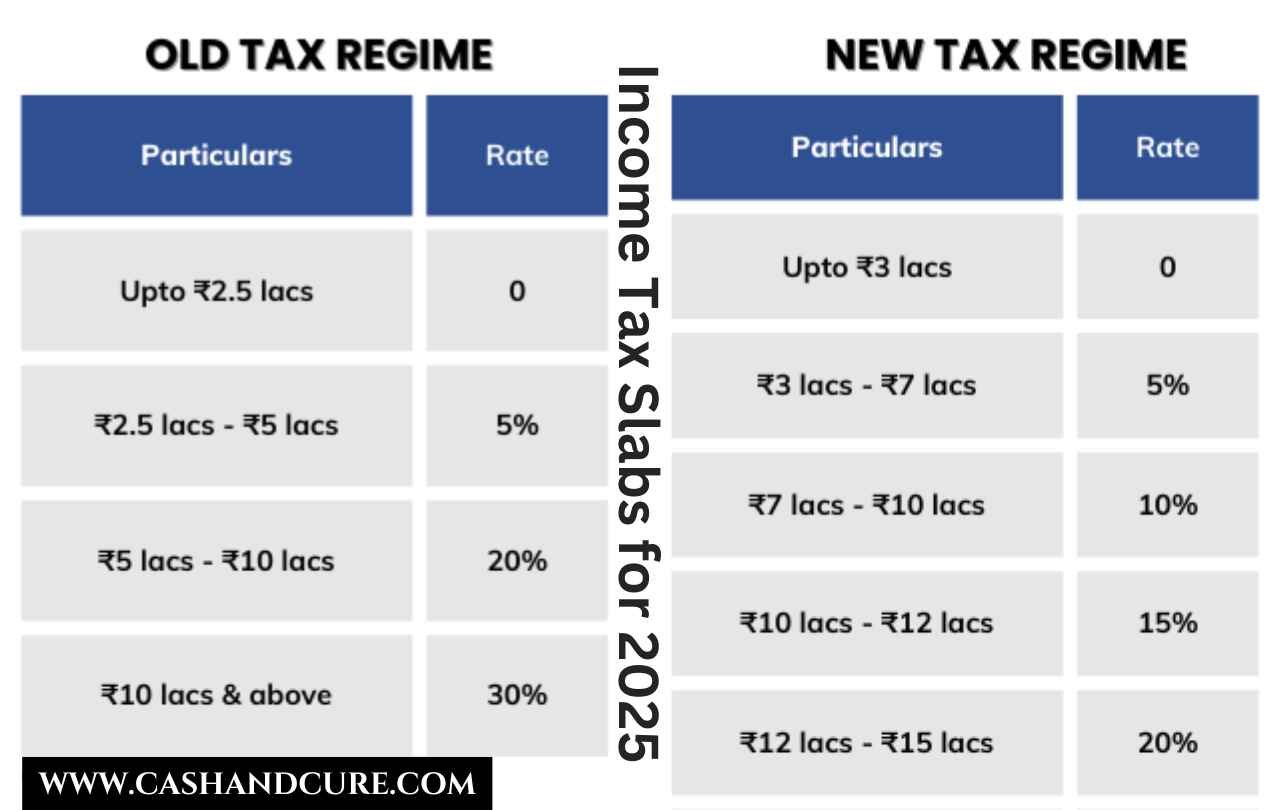
Income Tax Slab for 2025: New Regime
The new tax regime for the financial year 2024-25 has been designed to offer reduced rates and encourage more individuals to opt for a simplified tax filing process.
Income Tax Slabs for Individuals (Below 60 Years):
| Income Range (Rs.) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 – 3,00,000 | Nil |
| 3,00,001 – 6,00,000 | 5% |
| 6,00,001 – 9,00,000 | 10% |
| 9,00,001 – 12,00,000 | 15% |
| 12,00,001 – 15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 15,00,000 | 30% |
Key Features of the New Regime:
- No standard deductions or exemptions such as HRA, LTA, or 80C investments.
- Simplified filing process for taxpayers.
- Ideal for those who do not have significant deductions or exemptions to claim.
Income Tax Slabs for Senior* Citizens (60-80 Years)
| Income Range (Rs.) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 – 3,50,000 | Nil |
| 3,50,001 – 6,00,000 | 5% |
| 6,00,001 – 9,00,000 | 10% |
| 9,00,001 – 12,00,000 | 15% |
| 12,00,001 – 15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 15,00,000 | 30% |
Old Tax Regime
For individuals who prefer the old tax regime, the tax slabs remain unchanged. This regime allows taxpayers to claim exemptions and deductions under various sections, including Section 80C (Rs.1.5 lakh), Section 80D (medical insurance), and HRA.
| Income Range (Rs.) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 – 2,50,000 | Nil |
| 2,50,001 – 5,00,000 | 5% |
| 5,00,001 – 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 10,00,000 | 30% |
Note: The old regime benefits individuals who have high deductions or exemptions to claim, making it more suitable for salaried employees.
How to Choose Between Old and New Regime
Choosing between the old and new tax regimes can significantly impact your tax liability.
- Analyze Your Deductions:
If you claim deductions exceeding Rs.2.5 lakh annually (e.g., under 80C, HRA, and 80D), the old regime may be beneficial. - Lower Income Groups:
Taxpayers with income below Rs.7 lakh may benefit from the new regime due to the rebate under Section 87A, making their tax liability nil. - Simplified Filing:
If you want a hassle-free tax filing process with no need to declare exemptions, the new regime is ideal.
Implications of the Income Tax Slab for 2025
For Individuals:
- Middle-Income Groups: The reduced rates in the new regime aim to provide relief to middle-class taxpayers.
- Higher-Income Groups: The 30% tax rate remains unchanged for incomes above Rs.15 lakh.
For Businesses:
- Encourages a shift towards transparency and less reliance on tax-saving instruments.
- Promotes consumption by increasing disposable income.
For the Economy:
- A simplified structure reduces compliance costs.
- Higher disposable income may boost consumption and economic growth.
Tips to Reduce Tax Liability in 2025
Even with the simplified tax structure, there are ways to optimize your tax outgo:
- Utilize Section 80C:
If you opt for the old regime, invest in PPF, ELSS, NSC, or life insurance to claim deductions up to Rs.1.5 lakh. - Claim Section 80D Benefits:
Health insurance premiums qualify for deductions under the old regime. - House Rent Allowance (HRA):
Salaried individuals can claim HRA exemptions based on their rent and basic salary. - Use NPS for Retirement Savings:
Contributions to the National Pension System can earn deductions under Section 80CCD(1B). - Education Loan Interest:
Deduct the interest paid on education loans under Section 80E.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.